Congratulations to Dr. Nazema Siddiqui – Recipient of the 2024 DMC Diversity Matters Award
Dr. Siddiqui is being honored for her exceptional contributions to advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion in the microbiome sciences and women’s health.
EXTENDing Hope: Artificial Wombs for Safer Neonatal Development
For expectant mothers, going into labor early can be terrifying. Premature babies are at an increased risk for serious health problems. The earlier a baby is born, the higher risk of health challenges they have, including digestive issues, a weakened immune system, heart problems, and lung injuries, among others.
Highlights from the 4th Annual Genomics Scientific Retreat
The Duke School of Medicine Precision Genomics Collaboratory (PGC) held the fourth annual Genomics Scientific Retreat on December 13 in the Trent Semans Center Great Hall.
PGC Announces Student Pilot Grant Awardees
The Duke University School of Medicine Office of Biomedical and Graduate Education (OBGE) and Precision Genomics Collaboratory awarded 9 pilot grants of $2,000 each to SOM Biomedical PhD students. The goal of these grants is to support our students in scientific and educational efforts to bolster their graduate training experiences. These awards will help further research in a broad array of topics including glioblastomas, multiple sclerosis and pancreatic cancer. They will also help fund sequencing work and professional conferences.
Genomics ‘Unconference’ Creates New Way to Foster Innovation
This fall, Duke University faculty launched the inaugural Alpine Genomics Institute Unconference, a three-day meeting, held in the mountains of Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
Duke at ASHG
The American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) annual meeting is the largest human genetics and genomics meeting and exposition in the world. It provides a forum for presenting and discussing cutting-edge science in all areas of human genetics.
The meeting was held November 5-9 in Denver, Colorado. Several Duke faculty and trainees participated:
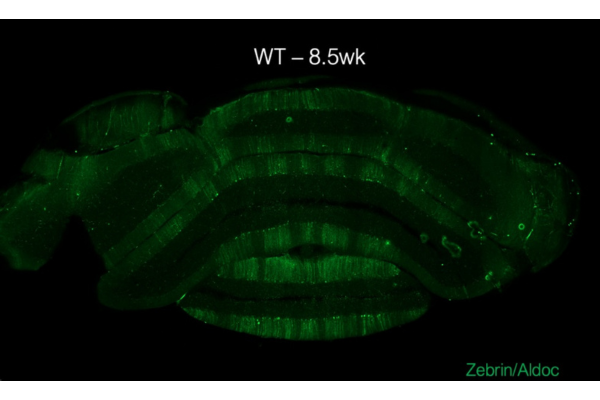
Striped gene expression pattern provides clues for neurodegenerative movement disorders
Spinocerebellar ataxias are a family of neurodegenerative disorders affecting muscle coordination and control.
Duke researchers are using single cell RNA sequencing technologies to better understand how these diseases form.
Duke-Led Model Identifies Pathogenic Variants in Cardiac Patients, Offers Diagnostic Hope
A new model developed by researchers at Duke University could help increase the number of patients receiving positive genetic test results, providing them with valuable information that could guide treatment decisions.
Genetic variants increase risk for chronic kidney disease in West Africans
Duke researchers led efforts in a collaborative case control and cohort study in Ghana and Nigeria on the prevalence of genetic risk factors for chronic kidney disease.
Svati Shah wins Gill Heart and Vascular Institute Award for Outstanding Contributions to Cardiovascular Research
The award recognizes notable and life-long achievements in research that have had a sustained impact on understanding cardiovascular biology and disease and/or that have changed the standard of cardiovascular clinical care.