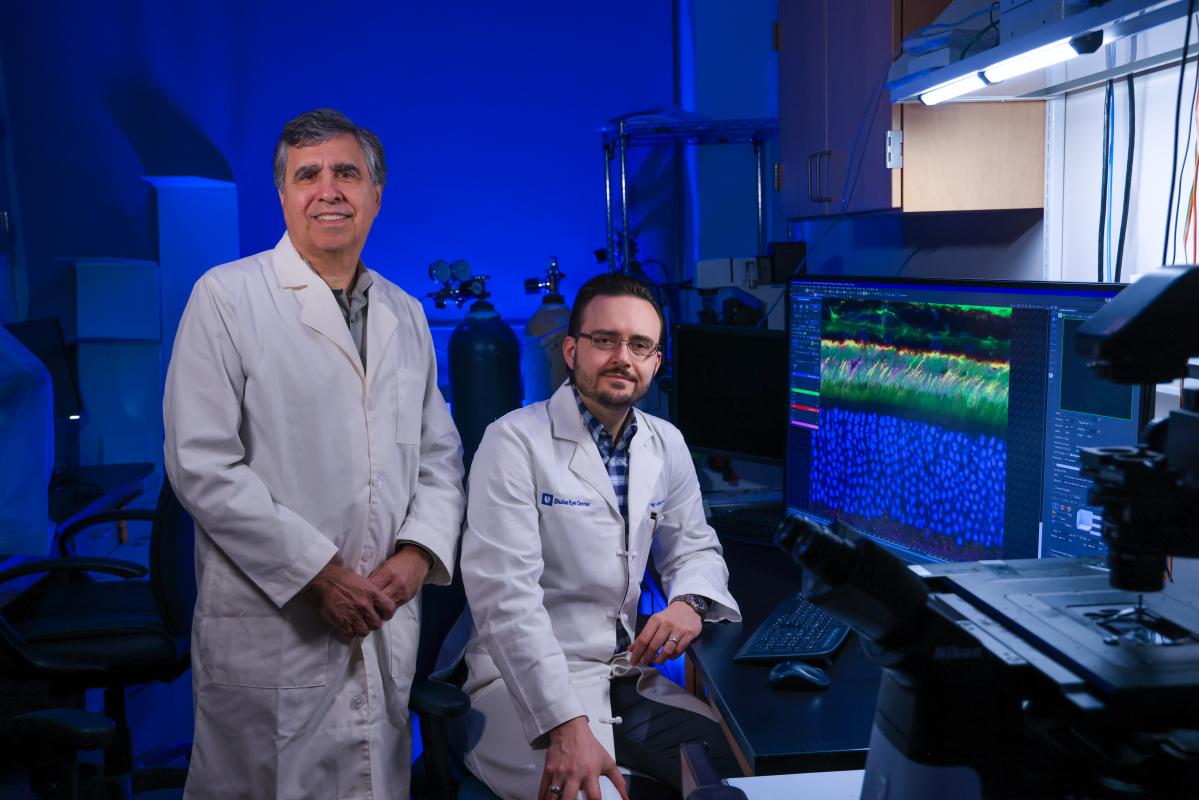
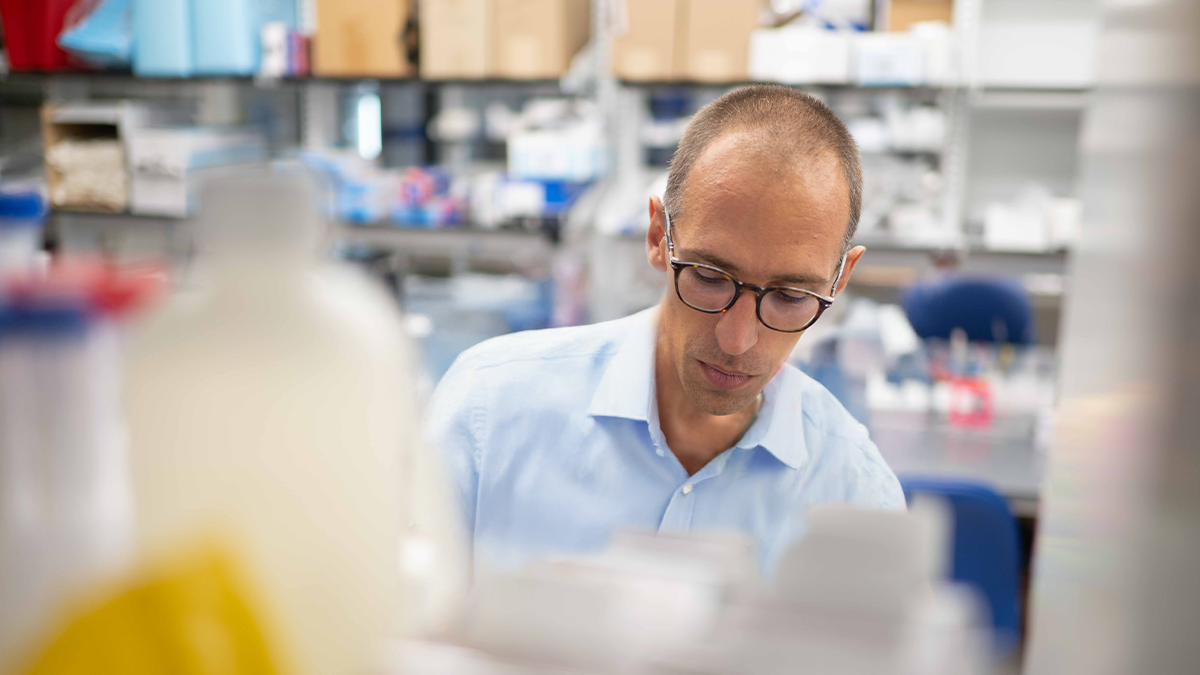
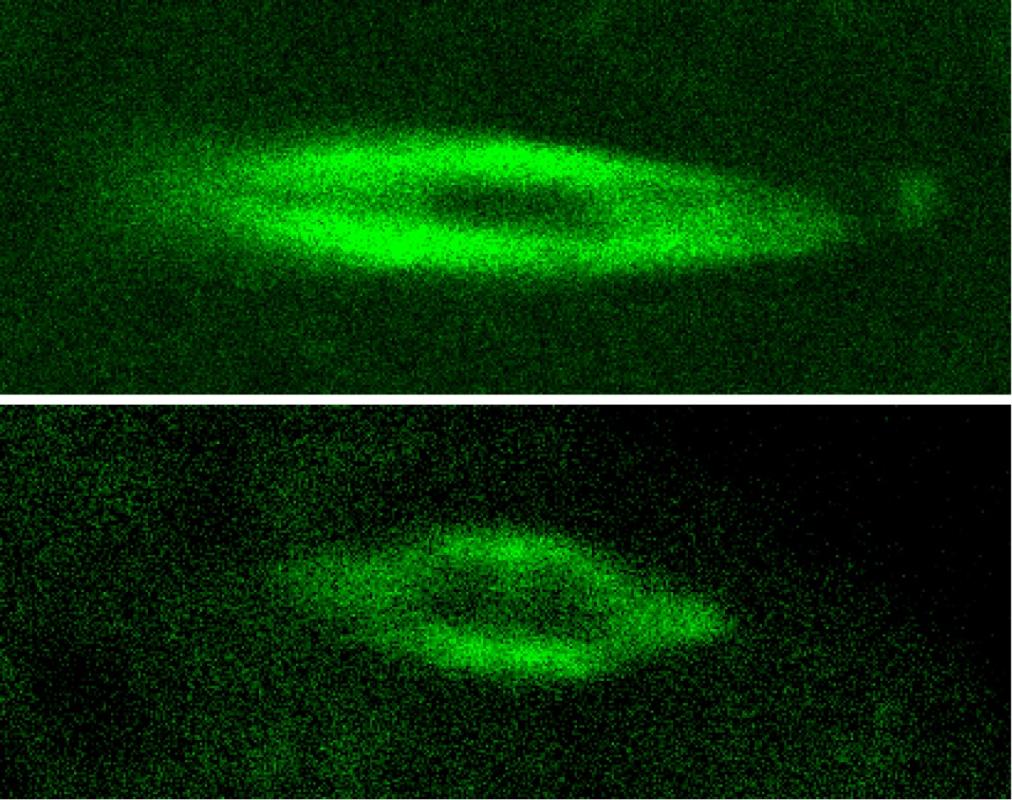
Eye disease mystery solved: How Best disease patients keep seeing clearly
Duke Eye Center discovery may explain how vision can stay surprisingly strong even when the eye’s structure is disrupted.
Miao and Derbyshire elected to the American Academy of Microbiology
Two faculty in the Duke University School of Medicine have been elected as fellows of the American Academy of Microbiology. Ed Miao, MD, PhD, Duke Health Distinguished Professor of Integrative Immunobiology, and Emily Derbyshire, PhD, Eads Family Professor of Chemistry, who has a secondary appointment in the Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, are among 63 new fellows elected for 2026.
Duke researchers find a new weakness in cancer cells: an 'in-between’ phase
One of the reasons cancer cells are so dangerous is their ability to shift between distinct “cell states,” a trick that helps them spread, survive treatment, and come back even after therapy initially works.
Discovery AI Ramps Up at Duke
Duke University School of Medicine has launched Discovery AI, an ambitious research initiative that aims to accelerate the application of artificial intelligence (AI) an
A nerve-based approach to helping older adults bounce back after surgery
Electrical nerve stimulation shows promise in preventing post-surgery delirium
New sensor shows how cells keep division on track
Cells inside our bodies divide constantly for growth and repair, but it’s a carefully controlled business. Mistakes can lead to diseases like cancer.
Researchers from Duke University School of Medicine have developed a sensor that reveals how cells maintain stability during this process. The sensor measures forces on motor proteins — tiny engines that help separate and organize chromosomes inside a structure called the spindle.
Restoring mitochondria shows promise for treating chronic nerve pain
Discovery at Duke School of Medicine suggests a new way to tackle the root cause of nerve pain by helping cells share energy.
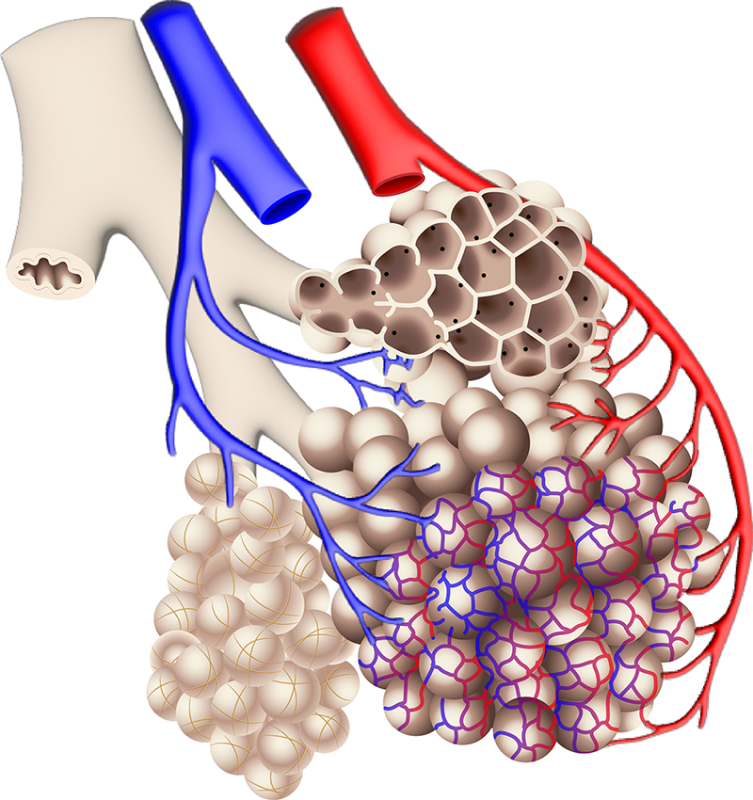
Duke School of Medicine launches $3.2 million effort to 3D-print a living lung
Lung model will mimic real breathing to study how co-infections can turn routine flu into life-threatening disease .
Researchers uncover how a killer fungus quietly invades the brain
Study shows a deadly fungus gets a two-week head start on the brain’s defenders. It points to a new strategy for boosting the immune system to fight Cryptococcus.
10 groundbreaking advances that grew out of HIV research
A new Nature Medicine paper highlights how 40 years of HIV research reshaped far more than the fight against one virus. What began as an urgent global health response helped fuel breakthroughs that now power treatments for cancer, tuberculosis, hepatitis, and even COVID-19 — thanks to sustained U.S. investment and collaboration across universities, industry, and government.